Male vs Female Soccer Injuries – Complete Guide (2025)
If you are looking for information on male vs female soccer injuries – this is for you.
In the world of soccer, both female and male athletes are exposed to a variety of injuries due to the sport’s high physical demands.
However, the types and frequencies of these injuries can differ significantly between genders, influenced by factors such as anatomical differences, hormonal influences, and variations in muscle strength and neuromuscular control.
By understanding these differences we can practice effective prevention to the unique needs of female and male soccer players. By examining the statistical differences in male vs female soccer injuries, we can have a better understand of how to avoid soccer injuries.
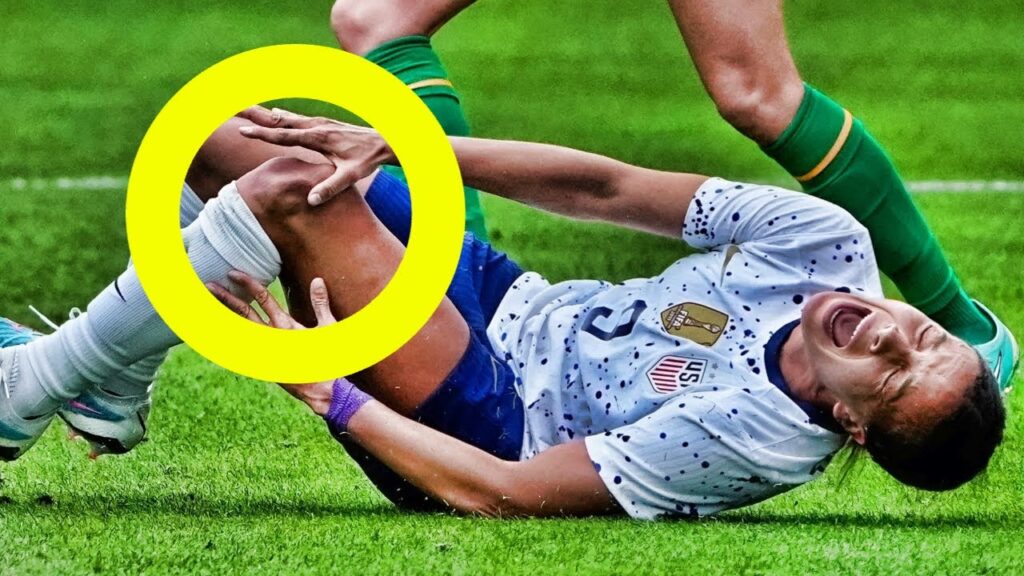

Male vs Female Soccer Injuries
In this article, you can read through all 5 sections or skip ahead to the topics that are most important to you. Make sure to stick around until the end, watch the video tutorial, and get your special free gift that is guaranteed to make you a better player.
- Women’s soccer injuries vs men’s
- Female Soccer Injuries
- Male Soccer Injuries
- Female vs Male Soccer Injury Statistics
- How to become a better soccer player, improve faster & achieve more
I hope this article gives you all you need about male vs female soccer injuries: Let’s get started!
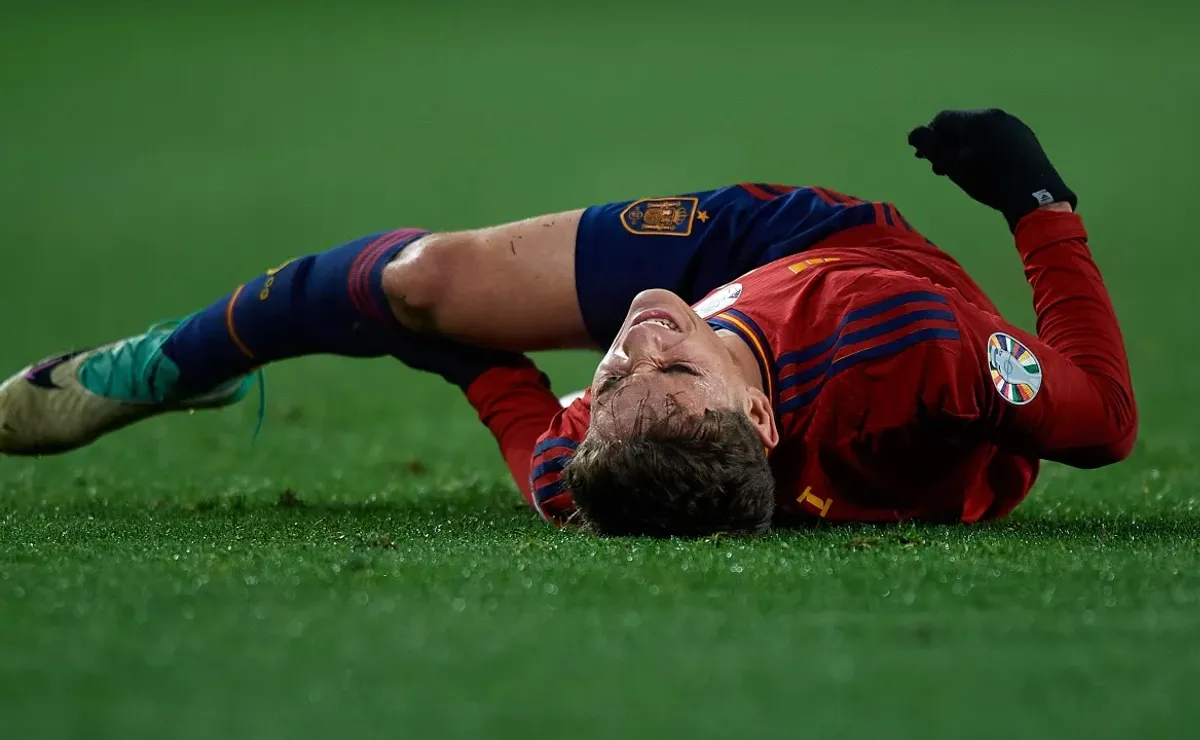

Women’s Soccer Injuries vs Men’s
There is a difference between female and male soccer injuries. Understanding these differences can help you tailor your training and injury prevention strategies to become a more resilient and effective player. Here are some key points:
Reasons for Differences
- Anatomical Differences:
- As mentioned, women generally have a wider pelvis, which affects the alignment of the lower extremities and increases stress on the knees.
- As mentioned, women generally have a wider pelvis, which affects the alignment of the lower extremities and increases stress on the knees.
- Hormonal Influences:
- Hormones like estrogen can affect ligament laxity, potentially making ligaments more susceptible to injury. The menstrual cycle can also influence injury risk, with some phases associated with higher vulnerability.
- Hormones like estrogen can affect ligament laxity, potentially making ligaments more susceptible to injury. The menstrual cycle can also influence injury risk, with some phases associated with higher vulnerability.
- Neuromuscular Control:
- Females may have differences in neuromuscular control, leading to variations in movement patterns that can increase injury risk. For instance, women might land from a jump with their knees more extended and valgus (inward), which can strain the ACL.
- Females may have differences in neuromuscular control, leading to variations in movement patterns that can increase injury risk. For instance, women might land from a jump with their knees more extended and valgus (inward), which can strain the ACL.
- Muscle Strength and Conditioning:
- Differences in muscle strength, particularly in the hamstrings and quadriceps, can affect joint stability. Women often have relatively stronger quadriceps compared to their hamstrings, which can imbalance the knee joint.
What You Can Do
- Strength Training:
- Focus on strengthening the muscles around your knees and hips. Pay extra attention to the hamstrings and glutes to support your knee stability.
- Focus on strengthening the muscles around your knees and hips. Pay extra attention to the hamstrings and glutes to support your knee stability.
- Proper Technique:
- Work on your landing and cutting techniques to ensure you are not putting unnecessary strain on your knees. Proper biomechanics can reduce the risk of ACL injuries.
- Work on your landing and cutting techniques to ensure you are not putting unnecessary strain on your knees. Proper biomechanics can reduce the risk of ACL injuries.
- Neuromuscular Training:
- Engage in drills that enhance your balance, coordination, and proprioception. These can help improve your overall movement patterns and reduce injury risk.
- Engage in drills that enhance your balance, coordination, and proprioception. These can help improve your overall movement patterns and reduce injury risk.
- Monitor and Adapt:
- Be aware of your menstrual cycle and how it might affect your training and injury risk. Adapt your training intensity and focus on recovery during more vulnerable times.
Understanding these differences and taking proactive steps can help you stay injury-free and perform at your best. Remember, prevention is key, and incorporating these strategies into your routine can make a significant difference in your soccer journey.
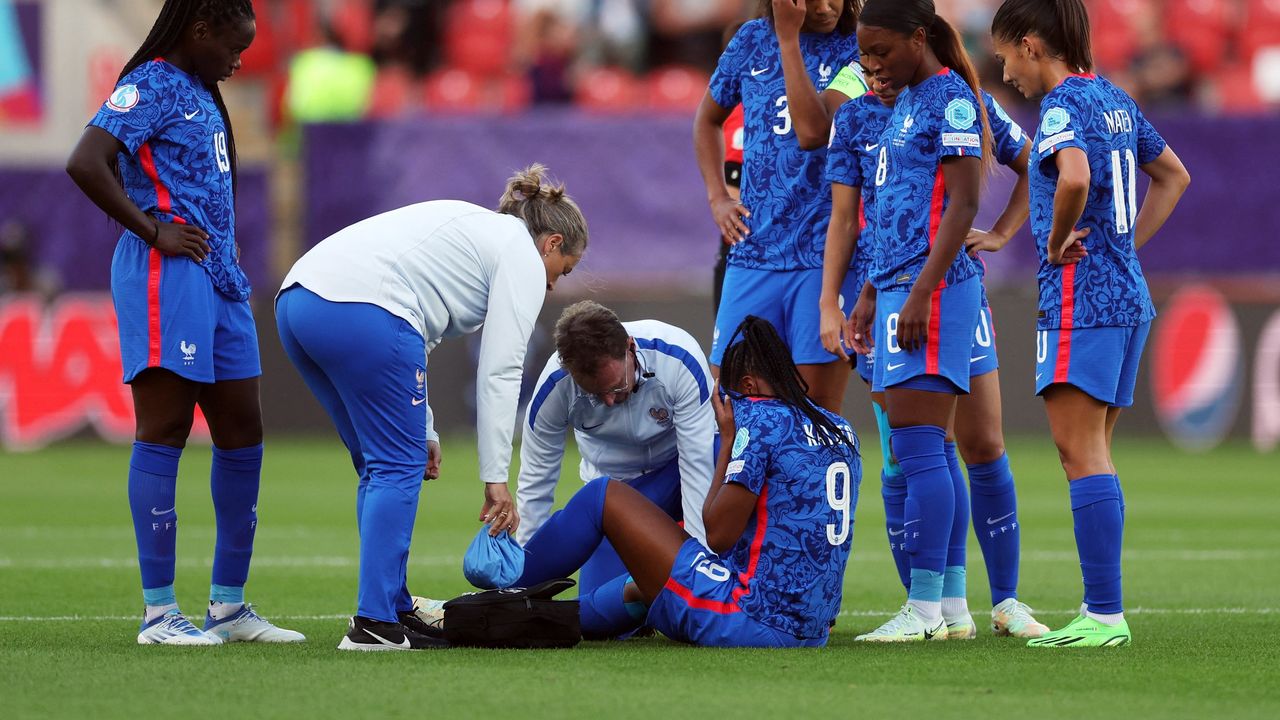

Female Soccer Injuries
Female soccer players face a unique set of common injuries. By understanding these and implementing preventative strategies, you can minimize your risk and maintain peak performance. Here are the most common injuries and how to prevent them:
1. Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
Prevention:
- Strength Training: Focus on building strength in the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes to support knee stability.
- Plyometric Exercises: Incorporate jumping and landing drills to improve neuromuscular control.
- Proper Technique: Learn and practice proper techniques for cutting, pivoting, and landing to reduce knee strain.
- Balance Training: Use exercises that improve your balance and proprioception, such as single-leg stands and stability ball exercises.
2. Ankle Sprains
Prevention:
- Ankle Strengthening: Perform exercises like calf raises and resistance band work to strengthen the muscles around your ankle.
- Balance Exercises: Incorporate balance board or single-leg exercises to improve ankle stability.
- Proper Footwear: Wear well-fitting, supportive cleats appropriate for the playing surface.
- Taping/Bracing: Consider taping or using an ankle brace during practices and games if you have a history of ankle sprains.
3. Stress Fractures
Prevention:
- Gradual Training Increase: Avoid sudden increases in training intensity or duration. Gradually build up your workload.
- Proper Nutrition: Ensure you are getting enough calcium and vitamin D to support bone health.
- Cross-Training: Incorporate low-impact activities like swimming or cycling to give your bones a break from repetitive stress.
- Footwear: Use proper footwear with good arch support and cushioning.
4. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS)
Prevention:
- Quad Strengthening: Strengthen your quadriceps with exercises like squats and leg presses to support your knee.
- Hip Strengthening: Strengthen your hip abductors and external rotators to improve knee alignment.
- Flexibility: Maintain flexibility in your hamstrings and calves to reduce knee stress.
- Proper Footwear: Wear shoes with good arch support and cushioning.
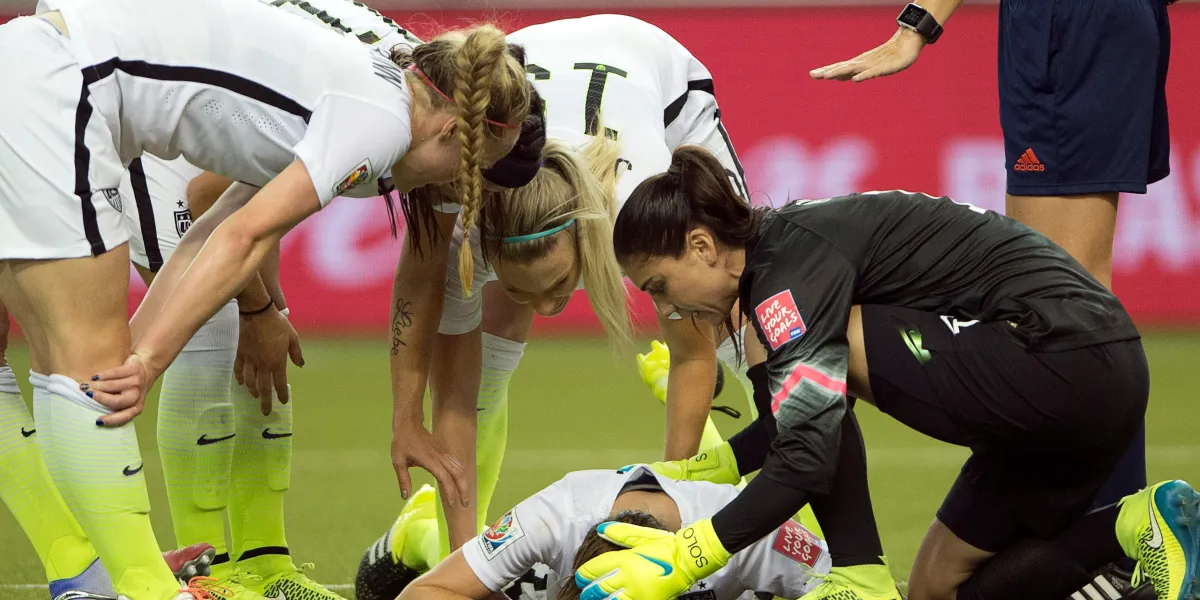

Male Soccer Injuries
Male soccer players, like their female counterparts, are susceptible to various injuries due to the physical demands of the sport. Knowing the most common injuries and how to prevent them can help you stay healthy and perform at your best.
Here are the most common injuries among male soccer players and strategies to prevent them:
1. Hamstring Strains
Prevention:
- Strength Training: Focus on hamstring-specific exercises like Nordic hamstring curls, leg curls, and deadlifts.
- Dynamic Warm-Up: Incorporate a thorough warm-up with dynamic stretches and activities to prepare your muscles.
- Flexibility Exercises: Regularly stretch your hamstrings to maintain flexibility.
- Gradual Progression: Increase the intensity and duration of your training sessions gradually to avoid overloading the muscles.
2. Groin Strains
Prevention:
- Strength Training: Focus on strengthening the groin muscles through exercises like adductor squeezes and side lunges.
- Dynamic Warm-Up: Include movements that engage the groin muscles, such as leg swings and lateral shuffles.
- Flexibility: Maintain flexibility in your groin area with regular stretching.
- Gradual Increase in Activity: Avoid sudden increases in training intensity to prevent muscle overuse.
3. Concussions
Prevention:
- Proper Heading Technique: Learn the correct technique for heading the ball to reduce impact on the head.
- Strength Training: Strengthen your neck muscles to help absorb impacts.
- Awareness: Be aware of your surroundings on the field to avoid collisions.
- Education: Know the symptoms of concussions and seek immediate medical attention if you suspect one.
4. Quadriceps Strains
Prevention:
- Strength Training: Strengthen your quadriceps with exercises like squats, leg presses, and lunges.
- Dynamic Warm-Up: Perform a proper warm-up that includes dynamic stretches targeting the quadriceps.
- Flexibility: Regularly stretch your quadriceps to maintain flexibility.
- Gradual Progression: Gradually increase the intensity of your training to prevent muscle overuse.
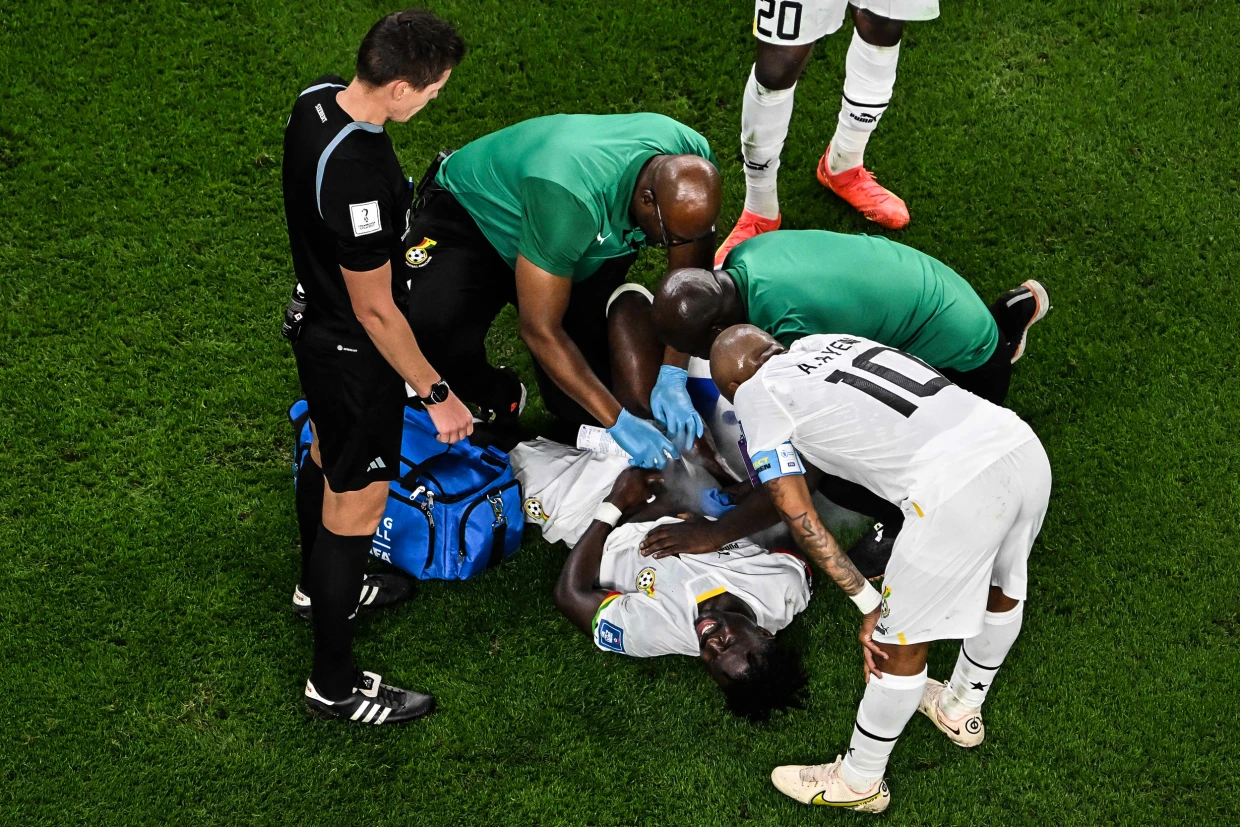

Female vs Male Soccer Injury Statistics
Understanding the statistical differences between female and male soccer injuries helps tailor prevention strategies more effectively. Here are some key statistics across various categories:
1. ACL Injuries
- Incidence Rate:
- Female soccer players are 2 to 8 times more likely to suffer from ACL injuries compared to male soccer players .
- Female athletes experience about 3 ACL injuries per 10,000 athletic exposures, while male athletes experience about 1 ACL injury per 10,000 athletic exposures .
2. Concussions
- Incidence Rate:
- Females have a higher rate of concussions, with studies indicating they are 1.4 times more likely to suffer a concussion compared to males in similar sports .
- In soccer, female players experience approximately 2.1 concussions per 10,000 athletic exposures, whereas male players experience about 1.5 concussions per 10,000 athletic exposures .
3. Stress Fractures
- Incidence Rate:
- Female athletes are at a higher risk for stress fractures, with studies suggesting rates 1.5 to 3.5 times higher than those in male athletes .
- The risk of stress fractures in female soccer players is around 3-4% per season, while for male players, it is about 1-2% .
4. Ankle Sprains
- Incidence Rate:
- Ankle sprains are common in both genders, but males have a slightly higher overall incidence. Male soccer players report about 5-6 ankle sprains per 1,000 athletic exposures, while female players report about 4-5 ankle sprains per 1,000 athletic exposures .
5. Hamstring Strains
- Incidence Rate:
- Hamstring strains are more common in male soccer players, with rates around 17-20% of all injuries. For female players, hamstring strains account for about 12-15% of all injuries .
6. Groin Strains
- Incidence Rate:
- Groin strains are also more frequent in male soccer players, making up about 12-16% of all injuries, compared to 6-10% in female players .
7. Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS)
- Incidence Rate:
- PFPS is more commonly reported in female athletes, with studies indicating they are about 2.5 times more likely to develop PFPS compared to male athletes .
Summary
- ACL Injuries: Significantly higher in females.
- Concussions: Higher in females.
- Stress Fractures: Higher in females.
- Ankle Sprains: Slightly higher in males.
- Hamstring Strains: Higher in males.
- Groin Strains: Higher in males.
- PFPS: Higher in females.
These statistical differences underline the importance of gender-specific training and prevention programs. Tailoring your approach to these risks can help mitigate the injury rates and keep players performing at their best.
Female soccer players might benefit more from ACL prevention programs and monitoring bone health, while male players might focus more on preventing muscle strains and maintaining flexibility.
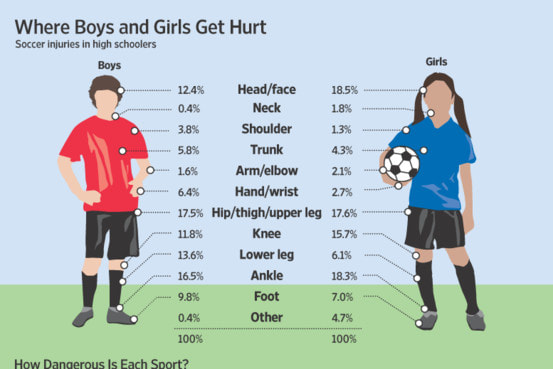
Female Soccer Injuries vs Male
Recognizing the statistical differences in injuries between female and male soccer players is essential for creating targeted prevention strategies.
Female players are more prone to ACL injuries and stress fractures, while male players experience higher rates of hamstring and groin strains, as well as slightly more frequent ankle sprains.
These insights highlight the importance of gender-specific training and conditioning programs.
By tailoring approaches to address these specific risks, we can help reduce soccer injury rates and ensure that all soccer players, regardless of gender, can enjoy a safer and more successful playing experience.

Common Questions
Here are some common questions related to male vs female soccer injuries:
What is the biggest difference in male vs female soccer injuries?
The most significant difference in male vs female soccer injuries often lies in the types of injuries and the areas most commonly affected. Female athletes tend to experience higher rates of knee injuries, particularly ACL tears, compared to males. This is largely due to differences in biomechanics, such as wider hips in females, differences in ligament structure, and hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle, which can make ligaments more lax and prone to injury. While men also suffer from a variety of injuries, including hamstring strains and ankle sprains, the higher frequency of knee injuries in females stands out. Additionally, female soccer players tend to experience more stress fractures and tendinopathies than their male counterparts.
Why do girls have more ACL injuries than boys in soccer?
Girls have a higher incidence of ACL injuries in soccer due to several factors, including anatomical and hormonal differences. Female athletes tend to have wider pelvises, which results in a greater angle in the knee (called the Q-angle), increasing the risk of knee injuries. The hormones estrogen and progesterone, which fluctuate during the menstrual cycle, can also affect ligament flexibility, making them more susceptible to damage. Additionally, females generally demonstrate lower levels of neuromuscular control and strength in their lower bodies compared to males, which may lead to less stable knee movements during cutting, jumping, or decelerating activities common in soccer.
Is men’s soccer more physical than women’s?
Men’s soccer is often considered more physically demanding in terms of speed, power, and physicality due to the difference in average size, strength, and endurance between males and females. However, women’s soccer is still highly competitive, with an emphasis on technical skill, tactical awareness, and stamina. Although men’s games tend to feature more high-speed contact and powerful tackles, women’s soccer has a similar level of intensity in terms of strategy, positioning, and endurance, despite some physical differences in terms of size and strength.
Do female soccer players have higher rates of knee injuries?
Yes, female soccer players generally have higher rates of knee injuries compared to male players, particularly ACL tears. Studies indicate that female athletes are more susceptible to knee injuries because of biological and biomechanical factors, including differences in the way they land from jumps, the angle of their knee joints, and their ligament laxity. The increased frequency of these injuries among women in soccer has led to more attention being paid to injury prevention strategies for female players, including strengthening exercises, proprioception training, and technique correction.
Why are females more prone to soccer injuries?
Females are more prone to soccer injuries due to several key factors, primarily related to biomechanics, hormonal fluctuations, and training methods. Anatomically, females often have wider hips, causing a higher Q-angle that can increase stress on the knees, making injuries like ACL tears more common. Hormonal variations, especially estrogen, also contribute to ligament laxity during certain points of the menstrual cycle, which can lead to instability and higher injury risk. Additionally, female athletes may not have the same level of neuromuscular strength and endurance in their legs and core as their male counterparts, leading to greater susceptibility to injuries like strains, sprains, and tears.
How many female soccer players tear their ACL?
The exact number of female soccer players who tear their ACLs varies, but studies show that females are anywhere from 4 to 6 times more likely to suffer an ACL injury compared to males in soccer. These injuries are particularly prevalent in sports that require rapid deceleration, pivoting, and jumping, which are common in soccer. Increased awareness and injury prevention programs focused on strengthening the muscles surrounding the knee, improving movement patterns, and reducing excessive stress on the joint have helped lower the rate of ACL tears among female soccer players.
What is the gender gap in sports injuries?
The gender gap in sports injuries refers to the increased susceptibility of female athletes to certain types of injuries compared to male athletes. Women typically experience higher rates of knee injuries, especially ACL tears, due to anatomical, physiological, and hormonal differences. Female athletes also have a greater likelihood of developing stress fractures, overuse injuries, and lower extremity injuries such as shin splints. While both male and female athletes face similar injury risks in some areas (e.g., ankle sprains and concussions), the higher rate of knee and lower extremity injuries among women highlights a significant gender gap in sports injuries, which has led to a greater emphasis on injury prevention, conditioning, and strength training for female athletes.

SOCCER PLAYERS
Want to become a better soccer player?
Watch this 3-minute video about discovering your true potential
Learn how to improve your skills, mindset, soccer IQ, and fitness—no matter your level. Start playing with confidence, earning respect, and impressing coaches today.
About Coach Dylan
I used to struggle with confidence in soccer, feeling slow, weak, and unmotivated. Coaches overlooked me, and friends made fun of my skills. At one point, I even quit.
But I decided to take control of my development. Through hard work, I transformed my game, earned league titles, awards, a college scholarship, and international caps.
Now, I share my lessons and help others improve through my YouTube channel (1/2 million subscribers), soccer coaching and personal training.

How To Play Soccer Better
Struggling to make progress in soccer or stay organized with your training?
The Soccer Success Planner will help you stay focused, motivated, and increase your chances of achieving your goals in soccer.
Success doesn’t happen accidentally. Use it to set clear goals, create a plan of action, and take control of your future. Learn more about the Soccer Success Planner.

How To Become A Better Soccer Player
Struggling to improve in soccer or unsure how to train effectively? Want to stand out and earn respect from teammates and coaches?
The Online Soccer Academy will get you better results in less time.
Thousands of players have already transformed their game in just 60 days. Learn more about how the online soccer academy.

Related Posts
Here are some related posts to help you gain more knowledge and helpful advice:
How To Become A Better Soccer Player in 1 Day
From Failure To Top Goal Scorer
Coach Dylan
Progressive Soccer
Thank you for reading this article:
Male vs Female Soccer Injuries – Complete Guide (2025)
